Stable blood sugar leads to better health and well-being.
Blood sugar levels and glucose spikes – these terms might immediately bring diabetes to mind. But this topic isn't just relevant for people with diabetes and has become a real trend in recent years. Did you know that your blood sugar determines how often you experience cravings, how often you get sick, or how much fat your body stores? No? Then it's high time we took a closer look at this topic together.

Basics: What is blood sugar?
Blood sugar describes how much glucose (sugar) is dissolved in the blood. Glucose is one of the body's most important energy sources . It is produced when carbohydrates from food are broken down into glucose molecules. When you eat carbohydrates, your blood sugar level automatically rises. Blood sugar levels fluctuate constantly, and it's perfectly normal for them to rise and be slightly elevated after eating. However, it becomes problematic when blood sugar levels rise too rapidly and then drop just as quickly.
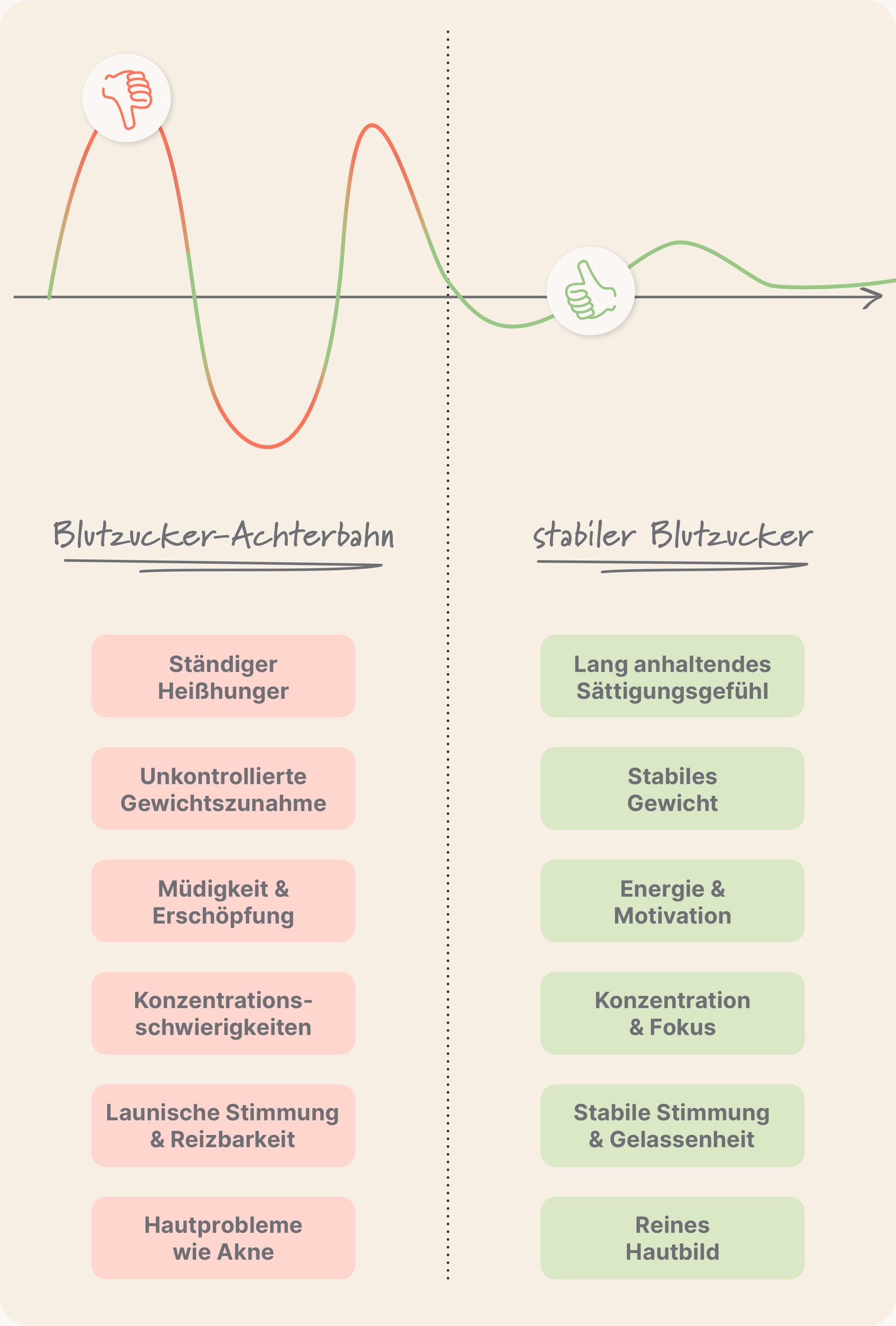
What are the effects of blood sugar fluctuations?
As soon as glucose enters a cell, it is converted into energy. The powerhouses responsible for this are microscopic organelles called mitochondria. Therefore, they are also known as the "powerhouses of the cell." However, our mitochondria only function optimally when there is a constant supply of glucose. If our blood sugar level spikes, the glucose is transported into the cells too quickly, and our mitochondria can no longer perform their function efficiently.
During a so-called glucose spike, more glucose enters the cells than our mitochondria can utilize. If this happens regularly, it leads to a range of negative effects , which vary greatly from person to person. In the short term, these range from cravings, sleep problems, constant hunger, and fatigue to migraines. In the long term, skin problems such as acne, cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and even an increased risk of cancer can result.
How your blood sugar affects your life:
The role of insulin
Insulin is a crucial hormone for regulating our blood sugar levels . After eating, glucose enters the bloodstream, raising our blood sugar levels. Insulin is released by the pancreas to control this increase. It enables cells to absorb glucose from the blood and convert it into energy or store it as glycogen in the liver and muscles. When needed, this glycogen can be converted back into glucose and released into the bloodstream to meet energy demands.
Insulin acts like a key that "unlocks" cells, allowing them to absorb glucose from the blood. If there is not enough insulin present, or if the cells do not respond to it (insulin resistance), the glucose circulates in the blood, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
In the long term, insulin is essential for keeping blood sugar levels stable. An imbalance – whether due to too much or too little insulin (as in diabetes) – can cause serious, chronic health problems.
Carbohydrates and blood sugar
Since carbohydrates lead to the formation of glucose, the question arises: Do all carbohydrates have a negative effect on blood sugar levels? No – thankfully not! In fact, there are different types of carbohydrates , some of which are more beneficial for our blood sugar than others.
Simple carbohydrates : These consist of simple sugar molecules such as glucose and fructose. They are digested quickly, leading to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels . Examples include table sugar, honey, fruits, and processed foods such as sweets, baked goods, juices, and soft drinks.
Complex carbohydrates : These consist of long chains of sugar molecules that are digested more slowly. This helps to keep blood sugar levels more stable . Complex carbohydrates are found in whole grain products, legumes, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Dietary fiber : Also known as indigestible carbohydrates, unlike sugar and starch, is not completely broken down in the intestines, resulting in a very slow release of glucose. This promotes a longer feeling of fullness and helps stabilize blood sugar levels . Dietary fiber comes from plant sources such as vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and fruits.
Keeping blood sugar stable
Depending on your diet, your blood sugar level rises slowly or almost rapidly after eating. Fortunately, there are a few simple tricks you can use to easily maintain stable blood sugar levels in your daily life.
Vinegar as a miracle cure for your blood sugar
The bitter truth: Our favorite temptations unfortunately trigger the strongest glucose spikes. Cookies, chocolate, and cakes, as well as pasta, bread, and rice, are the biggest enemies of our blood sugar levels.
However, there is a little miracle worker that can significantly minimize the blood sugar spikes after consuming these foods, and it's incredibly inexpensive: vinegar . Yes, you heard right! Studies show that a tablespoon of vinegar (about 10 milliliters) before a sugary or starchy meal can lower blood sugar by up to 20% . It also stimulates our fat burning.¹ Sounds like fantasy, but it's scientifically proven!
Vinegar's blood sugar-lowering effect stems from its ability to slow the breakdown of sugars and starches into glucose . This prevents our mitochondria from being overwhelmed by a flood of glucose. Furthermore, the vinegar reaches our muscles via the bloodstream, stimulating them to absorb glucose molecules and store them for later use. This also reduces the burden on the mitochondria due to less freely circulating glucose.²
To consume vinegar quickly and easily, simply dissolve it in a glass of water. While any type of table vinegar (5% acetic acid) will work, many prefer the taste of apple cider vinegar.
The order counts
Whether and how severe glucose spikes occur depends not only on what we eat, but also on the order in which we consume the different foods. The "meal sequence" theory offers valuable guidance here. This theory recommends structuring meals so that we start with vegetables , then consume proteins and fats , before finally consuming carbohydrates . This order has several advantages: It prevents a rapid and steep rise in blood sugar levels and thus also ensures a longer-lasting feeling of satiety. Scientific research has shown that following this order can reduce post-meal glucose spikes by an astonishing 73%. This effect is comparable to the effect of diabetes medications on blood sugar control.³
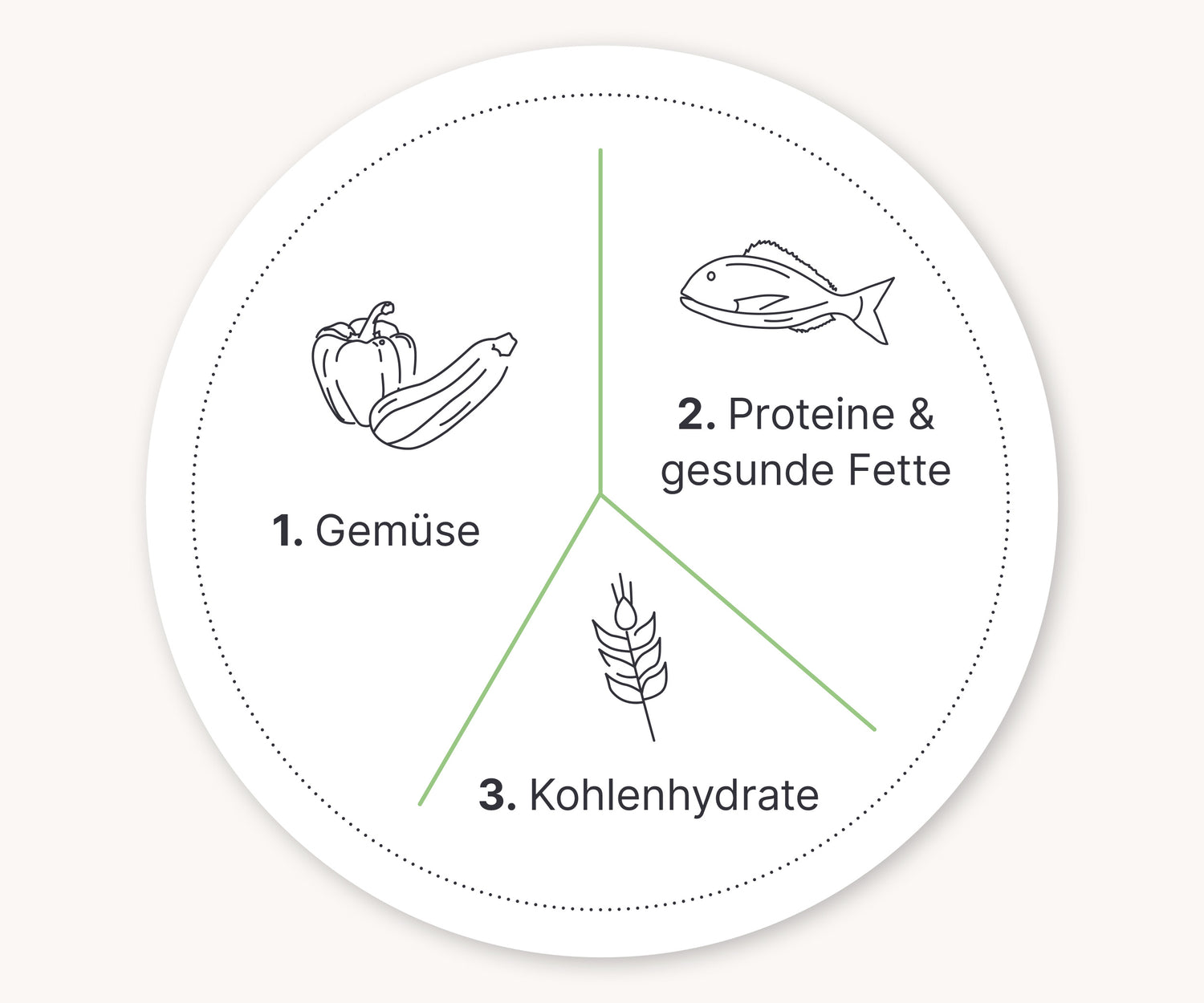
This trick is ideal for eating in a restaurant or at a buffet on vacation. Start your meal with a salad. The bread should be eaten last! In restaurants, bread is often served right at the beginning, which is intended to stimulate our appetite.
Sounds promising, right? And the best part: there are many more simple tricks that can make a big difference with minimal effort. In our e-book "The SHEKO Secret," we share these tips with you and also offer valuable expert knowledge for a balanced and healthy life. Get one of our two blood sugar starter kits now and receive the guide for free!
A little helper for on the go
Our new, improved Blood Sugar Balance with the patented active ingredient Reducose® ensures that you no longer have to worry about hidden carbohydrates and glucose spikes, even when you're on the go. Say goodbye to cravings, constant hunger, low mood, and that feeling of fullness after eating!
Reducose® – a natural extract from the white mulberry leaf – has been scientifically proven to lower the rise in your blood sugar levels after consuming sugar and starch by up to 40% . This innovative ingredient is still a well-kept secret, but its impressive effects have already been confirmed in numerous research studies.
Your blood sugar is gently regulated, keeping it within the optimal, healthy range. This effect is immediately measurable, for example with a continuous glucose monitor. Chromium and cinnamon remain part of the formula, as they too have been proven to contribute to healthy blood sugar levels.
These foods will keep your blood sugar levels stable.
Foods that lower or stabilize blood sugar are usually rich in fiber or protein , have a low glycemic index, or contain specific nutrients.
Just to reiterate: Dietary fiber helps to keep our blood sugar levels constant by slowing down glucose absorption and thus preventing a rapid rise in blood sugar.
Protein-rich foods are also beneficial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Proteins slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and reduce the rate at which they are converted into glucose. This leads to a slower rise in blood sugar levels after meals.
The glycemic index (GI) is a scale that indicates how quickly and significantly a food raises blood sugar levels. The GI compares the rise in blood sugar after consuming a food to the rise that occurs after consuming a reference intake of pure glucose. A low GI does not necessarily mean that a food is healthy, but it can be a useful indicator for blood sugar regulation.
- whole grain products
Oatmeal, quinoa and wholegrain bread have a low glycemic index and promote stable blood sugar levels.
- Legumes
Lentils, chickpeas, beans and peas are rich in fiber and protein, which slows down glucose absorption.
- Non-starchy vegetables
Broccoli, spinach, kale and zucchini contain few carbohydrates and many fiber.
- Berries
Blueberries, strawberries and raspberries have a low glycemic index and are rich in antioxidants.
- Nuts and seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds and flax seeds offer healthy fats and fiber that help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Fatty fish
Salmon, mackerel and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have an anti-inflammatory effect and can positively influence blood sugar levels.
- Fish, eggs, dairy products
These are excellent sources of protein. Protein helps control blood sugar spikes after meals and ensures a long-lasting feeling of fullness.
- Avocados
These contain healthy fats and fiber, which support blood sugar regulation.
- Cinnamon
Studies show that cinnamon can lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.⁴
- Green tea
It can help improve insulin sensitivity and stabilize blood sugar levels.

Our Balance Shakes contain plenty of protein, healthy fats and a sophisticated combination of nutrients that help keep your blood sugar constant.
Measure blood sugar
Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for people with diabetes to track and control their blood sugar levels. It helps them understand and adjust how diet, medication, and lifestyle factors affect blood glucose. Monitoring can also be beneficial for individuals who want to keep track of their blood glucose levels for a period of time for health or preventative reasons.
Methods for measuring blood glucose
A small device that measures blood sugar levels using a single drop of blood. You insert a test strip into the device, prick your finger with a lancing device to obtain a small drop of blood, and apply it to the test strip. Within seconds, your current blood sugar level appears on the meter's display.
A sensor is inserted under the skin and continuously measures your blood sugar level over an extended period. The data is transmitted to a monitor or smartphone.
While finger-prick blood glucose testing only provides a snapshot of blood sugar levels, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) shows a long-term trend. Blood glucose values are expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) or millimoles per liter (mmol/l).
Ideal blood sugar levels
In people without diabetes , fasting blood glucose levels, i.e., after eight hours without food, are normally below 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) or below 5.5 millimoles per liter (mmol/l). Two hours after a meal, blood glucose levels should ideally be below 140 mg/dl (or 7.8 mmol/l).⁵
On an empty stomach (at least eight hours without food), before meals
60 - 100 mg/dl or
3.3 - 5.5 mmol/l
Two hours after meals
90 - 140 mg/dl or
5.0 - 7.8 mmol/l
If there are signs that your blood sugar levels are falling outside the normal range, an HbA1c test is usually performed. This test provides information about your average blood sugar level over the past 8 to 12 weeks and helps to diagnose possible diabetes or adjust your medication.
Summary and Conclusion
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for your health and well-being, and this extends far beyond diabetes. Blood sugar fluctuations can lead to cravings , fatigue, and long-term health problems . Simple tricks like paying attention to the macronutrient order at mealtimes and consuming fiber- and protein-rich foods can help keep blood sugar stable. Additionally, our Blood Sugar Balance capsules with natural micronutrients and vitamins support your blood sugar levels.
Successful weight loss despite diabetes
"Being overweight has been an issue for me since childhood. I weighed 80 kilograms when I was just 12. But nobody ever knew what was wrong. Everyone was baffled as to why the number on the scale kept increasing year after year. My diet was actually quite normal." - Ramona
Here you can find out how Ramona managed to lose weight successfully with SHEKO despite having diabetes.

Sources:
-
¹
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1756464618300483 -
²
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31221273/ -
³
https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/38/7/e98/30914/Food-Order-Has-a-Significant-Impact-on -
⁴
https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12937-015-0098-9 -
⁵
https://www.helios-gesundheit.de/magazin/news/blutzuckerwerte-und-ihre-bedeutung












